Imagine this: You’re enjoying a hearty plate of chapati ndengu, feeling full and satisfied. But little do you know, that seemingly harmless meal could be wreaking havoc on your body.
This is the reality for many people living with Celiac Disease, an autoimmune condition that affects how your body reacts to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Gluten is everywhere—chapatis, mandazis, soups and even our local brews. For someone with celiac disease, eating even a tiny amount of gluten triggers a serious immune reaction that damages the small intestine. It’s not just about avoiding wheat—it’s a lifelong health condition that requires strict gluten-free living.

Despite this, many people in East Africa have never heard of celiac disease, and those suffering from it often go undiagnosed for years. Here are some surprising facts that might just change the way you see gluten and celiac disease:
1️⃣ Most People with Celiac Disease Don’t Even Know They Have It
Imagine feeling constantly bloated, fatigued, or suffering from unexplained weight loss for years—without ever realizing gluten is the culprit. Studies estimate that 83% of people with celiac disease are undiagnosed or misdiagnosed with conditions like IBS, anemia, or chronic fatigue. Since celiac disease shares symptoms with many other conditions, it often takes time before a proper diagnosis is made.
(Source: Beyond Celiac)
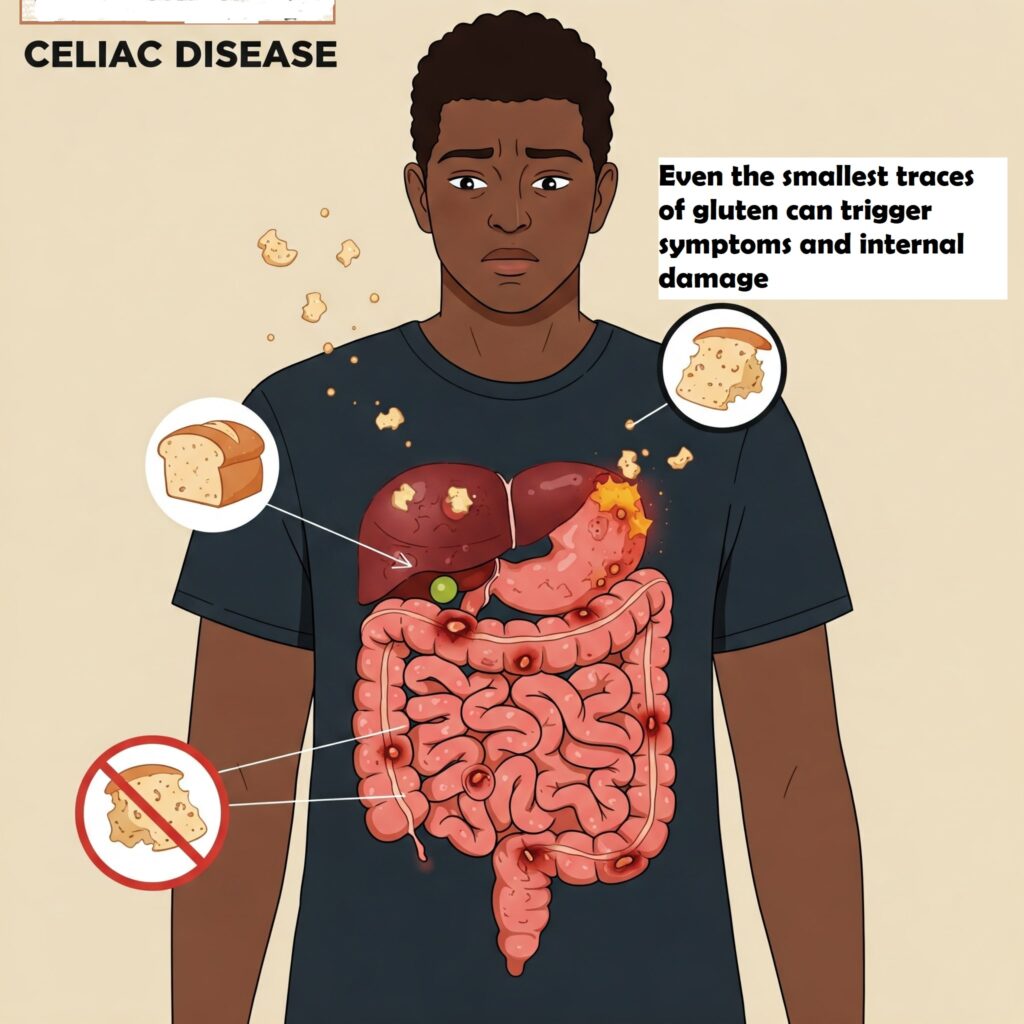
2️⃣ Even Tiny Crumbs of Gluten Can Be Harmful – Cross-Contamination is a Big Deal
For someone with celiac disease, avoiding gluten isn’t just about skipping bread. Even the smallest traces of gluten can trigger symptoms and internal damage. That means:
✅ Sharing a toaster—even a few crumbs left behind can be harmful.
✅ Eating fries cooked in the same oil as breaded foods—cross-contact makes them unsafe.
✅ Using the same knife for butter or jam—traces of gluten can linger.
✅ Cooking with the same spoon or pot that touched gluten—residue can transfer easily.
This is why people with celiac need dedicated utensils, cooking spaces, and extra caution when eating out.
3️⃣ It Can Take 6–10 Years to Get Diagnosed
Celiac disease isn’t always the first condition doctors consider when someone presents with symptoms, leading to long delays in diagnosis. On average, it takes 6 to 10 years to get properly diagnosed. That’s nearly a decade of unnecessary suffering simply because the condition isn’t widely recognized or tested for early. Raising awareness can help shorten this timeline and get people the help they need sooner.
(Source: Beyond Celiac)

4️⃣ Gluten Can Be in Skincare & Medications, Not Just Food
Gluten isn’t just in wheat, bread, or pasta—it can hide in skincare, cosmetics, and even medications. While gluten can’t be absorbed through the skin, products like lip balm, toothpaste, and hand lotions can be ingested accidentally. Some medications also contain gluten as a filler, making label-checking a must for people with celiac disease.

5️⃣ Celiac Can Lead to Brain Fog & Neurological Disorders
Ever felt like your brain is in a haze, struggling to focus or remember things? That’s brain fog, and for some people with undiagnosed celiac, it’s a major symptom. Celiac disease can also lead to memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and nerve damage (neuropathy). Since the gut and brain are closely connected, gluten can have effects beyond digestion.
(Source: National Institutes of Health)
6️⃣ Celiac Disease Increases the Risk of Osteoporosis
Because gluten damages the small intestine, it prevents the body from properly absorbing calcium and Vitamin D—leading to weak bones (osteoporosis). Many people don’t realize their bones are at risk until fractures start happening. That’s why early diagnosis and a nutrient-rich gluten-free diet are key to preventing long-term complications.
(Source: National Osteoporosis Foundation)
7️⃣ Children with Celiac May Have Growth Issues
For children, undiagnosed celiac disease can stunt growth and delay puberty because their bodies aren’t absorbing enough nutrients. Some kids are mistakenly diagnosed with malnutrition when, in reality, their intestines are damaged by gluten. Going gluten-free allows their bodies to start healing, leading to healthier growth and development.
(Source: Celiac Disease Foundation)
8️⃣ You Can Have Celiac Without Any Digestive Issues
Many people assume celiac disease always causes stomach pain or diarrhea. But for some, it shows up in completely different ways—infertility, depression, joint pain, migraines, or even a persistent skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis). Others have no obvious symptoms but still suffer silent internal damage. This is why celiac can be so hard to detect.
(Source: Mayo Clinic)
9️⃣ Celiac Disease is the Only Autoimmune Condition with a Known Trigger—But Managing It Can Require More Than Just Diet
Unlike other autoimmune diseases, which have unknown causes, celiac disease has a clear trigger: gluten. The only long-term treatment is a strict gluten-free diet. However, some people may still need medications—especially if they have nutrient deficiencies, accidental gluten exposure, or complications like osteoporosis. Supplements and medical care play a crucial role in recovery for those with severe cases.

🔟 It Affects More Women Than Men
Celiac disease disproportionately affects women, with studies showing that women are nearly three times more likely to be diagnosed than men. The reason isn’t fully understood, but researchers believe it could be linked to hormonal differences and the way autoimmune diseases generally affect women more often. For many women, symptoms like infertility, irregular menstrual cycles, or early osteoporosis may be the first signs of undiagnosed celiac.

Why This Matters
Gluten-free isn’t a fad, a diet trend, or just a personal choice—it’s a medical necessity for people with celiac disease. In East Africa, where awareness is low and gluten-free options are limited, many people are suffering in silence, misdiagnosed, or struggling to navigate a diet that’s so different from the norm.
If this sounds like someone you know—maybe a friend, a child, or even yourself—it’s worth looking into. Getting tested could be life-changing.
Share this with someone who might need to read it. Let’s spread awareness together. 💙
